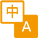CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4, designated CD152), is a type I transmembrane T cell inhibitory molecule that is a member of the Ig superfamily. Human or mouse CTLA-4 cDNA encodes 223 amino acids (aa) including a 35 aa signal sequence, a 126 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with one Ig-like V-type domain, a 21 aa transmembrane (TM) sequence, and a 41 aa cytoplasmic sequence. It is found as a covalent homodimer of 41-43 kDa Within the ECD, human CTLA-4 shares 68%, 71% and 83?86% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat and porcine/bovine/rabbit/feline/canine CTLA-4, respectively. A 174 aa form that lacks TM and cytoplasmic sequences (sCTLA-4) is possibly secreted (3-5). Isoforms of 56-79 aa that mainly contain parts of the cytoplasmic domain are reported. In mouse, an isoform lacking the Ig-like domain has ligand-independent inhibitory activity and is termed liCTLA-4. CD28, which is structurally related to CTLA-4, is constitutively expressed on naïve T cells and promotes T cell activation when engaged by B7-2 on antigen-presenting cells (APC) within the immunological synapse (IS) . In contrast, CTLA-4 is recruited from intracellular vesicles to the IS beginning 1-2 days after T cell activation.
高纯度、高活性、低内毒素、高批间一致性
产品数据
Tris-Bis PAGE
-25 ~ -15℃保存,收到货之后有效期1年。 复溶后, 无菌条件下,-85 ~ -65℃保存,3个月有效期。