T cell surface antigen CD2 is a type I glycoprotein belonging to the Ig superfamily and is expressed on T cells, NK cells, B cells and some antigen presenting cells. CD2 functions as an activator of T lymphocytes and thymocytes. Mature human CD2 consists of a 185 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD), a 26 aa transmembrane segment, and a 116 aa cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular domain is composed of two immunoglobulin-superfamily domains with highly-charged binding regions. Within the ECD, human CD2 shares 47% and 48% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat CD2, respectively. It interacts with both CD58 and CD59 directly to activate T cells and their adhesion pathways. The conformational flexibility of the CD2 molecule affects function through the conformational status of the adhesive ligands. Together with PSTPIP1, CD2 works to regulate T cell activation. These two proteins colocalize with a second CD2-binding protein to signal immunological synapse formation in T cells. CD2 is an adhesion molecule present on the cell surface of T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and B cells; and its interaction with CD58 on antigen-presenting cells plays an important role in their immune reaction. CD2-CD58 interactions play a critical role in the anti-tumor immune response, and restoration of this signaling is an important strategy for anti-tumor therapy.
高纯度、高活性、低内毒素、高批间一致性
产品数据
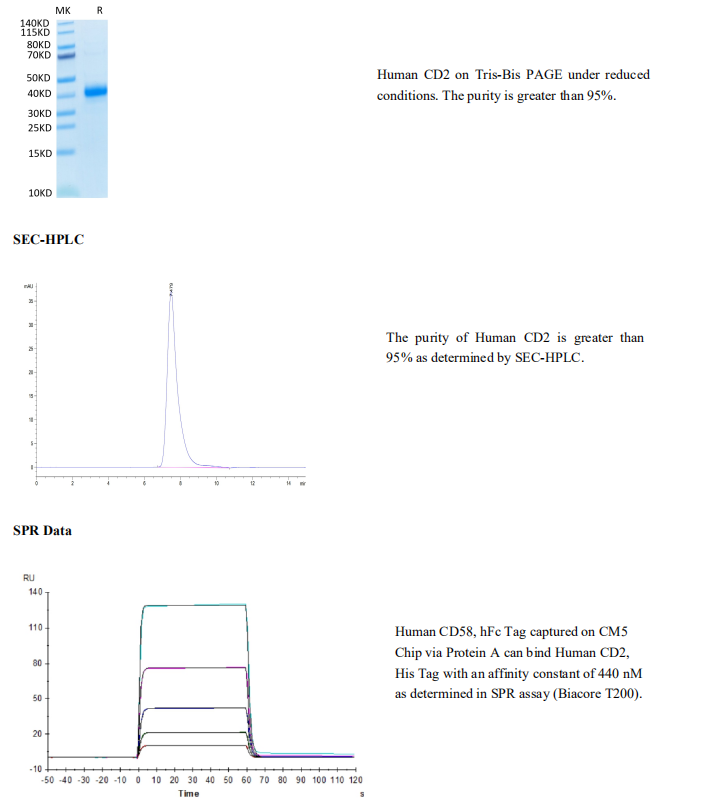
Tris-Bis PAGE
-25 ~ -15℃保存,收到货之后有效期1年。 复溶后, 无菌条件下,-85 ~ -65℃保存,3个月有效期。
