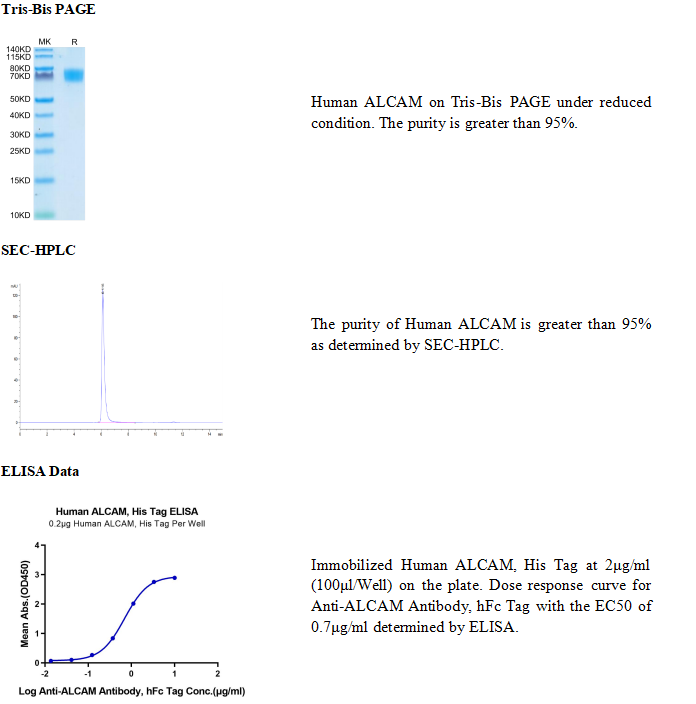
ALCAM (activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule), designated CD166 , is a 100‑110 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein and a member of the Ig CAM family within the immunoglobulin superfamily. ALCAM is expressed on thymic epithelium, microvascular endothelium, activated lymphocytes and monocytes, and monocyte‑derived dendritic cells. Human ALCAM cDNA encodes 583 amino acid (aa), including signal peptide (27 aa), extracellular domain (ECD, 500 aa) with two V‑type and three C2‑type Ig‑like domains, transmembrane (22 aa) and cytoplasmic (34 aa) domains. A secreted isoform in endothelial cells that is truncated at aa 133 (sALCAM) antagonizes full‑length ALCAM. ALCAM mediates low‑affinity adhesion with itself or the cysteine‑rich scavenger receptor CD6 to regulate T cell development, immunological synapses (IS), and cell migration through endothelial junctions. ALCAM on thymic epithelia mediates adhesion to CD6 on CD4+CD8+ T cells. Adhesion of ALCAM‑expressing antigen presenting cells and CD6‑expressing T cells stabilizes the early IS, while later it enhances CD3 effects on T cell proliferation, CD25 expression, and Th1 commitment. High ALCAM expression at the blood‑brain barrier in active multiple sclerosis, and its mouse model (EAE), promotes leukocyte migration to the brain. High ALCAM expression on melanoma cell lines appears to be pro‑metastatic, but anti‑metastatic activity has been reported in breast cancer.
高纯度、高活性、低内毒素、高批间一致性
产品数据
-25 ~ -15℃保存,收到货之后有效期1年。 复溶后, 无菌条件下,-85 ~ -65℃保存,3个月有效期。