CD200, also known as OX-2, is a 45 kDa transmembrane immunoregulatory protein that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD200 is widely but not ubiquitously expressed. Its receptor (CD200R) is restricted primarily to mast cells, basophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells, which suggests myeloid cell regulation as the major function of CD200. CD200 knockout mice are characterized by increased macrophage number and activation and are predisposed to autoimmune disorders. CD200 and CD200R associate via their respective N-terminal Ig-like domains. In myeloid cells, CD200R initiates inhibitory signals following receptor-ligand contact. In T cells, however, CD200 functions as a costimulatory molecule independent of the CD28 pathway. Several additional CD200R-like molecules have been identified in human and mouse, but their capacity to interact with CD200 is controversial . Several viruses encode CD200 homologs which are expressed on infected cells during the lytic phase . Like CD200 itself, viral CD200 homologs also suppress myeloid cell activity, enabling increased viral propagation.
高纯度、高活性、低内毒素、高批间一致性
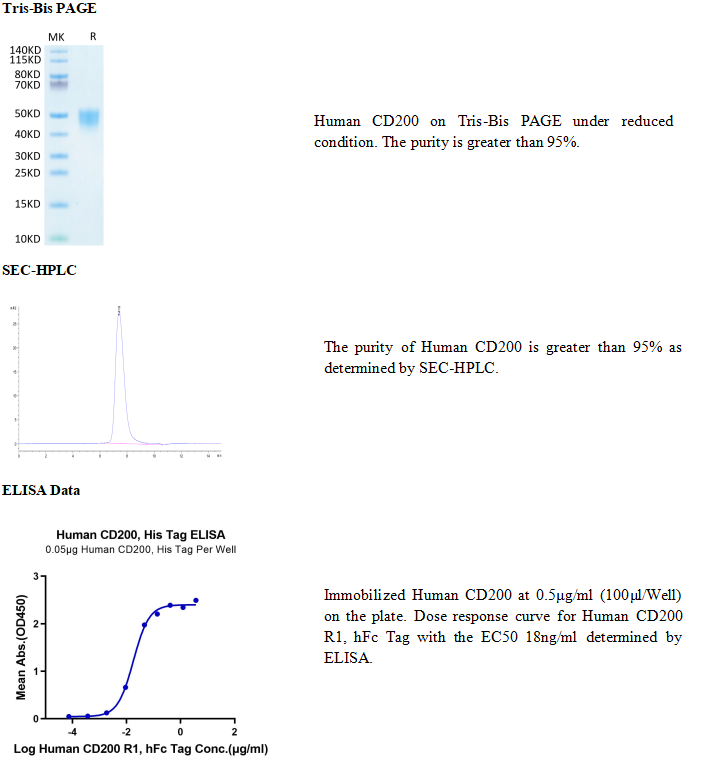
产品数据
-25 ~ -15℃保存,收到货之后有效期2年。 复溶后, 无菌条件下,-85 ~ -65℃保存,3个月有效期。
